고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문
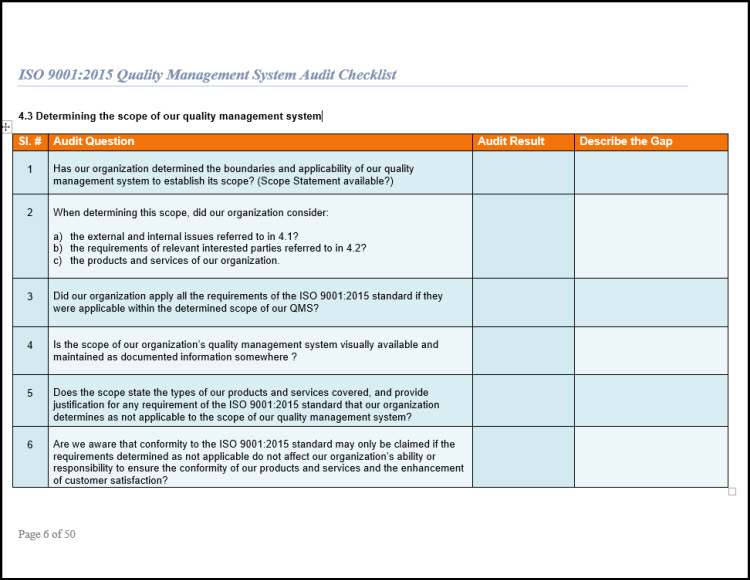
- Iso 9001 2015 Management Review Checklist
- Iso 9001 2015 Management Review Template
- Iso 9001 Management Review Checklist Form
- Iso 9001 2015 Checklist Pdf
- Quality Management Review Template
What is a management review for ISO 9001? The management review process requires Top management must periodically review the QMS to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness while addressing the possible need for changes to quality policy, objectives, targets and other elements of the QMS.
Our range of templates cover the requirements of ISO 9001:2015, ISO and ISO, and offer an easy way to implement your next management system. 9.3 Management Review 9.3.1 Management Review - General. Top management must periodically review the management system to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness. ISO 9001:2015 and Management Review Checklist Choice Consulting Management Review Guidelines Starting with ISO 2008 and related standards such as AS9100 and ISO-TS-29001, the management review can no longer simply be a report prepared by someone and looked over by the top manager.
The management review should include representation from Top management, functional managers, line managers, process owners, process users and action owners.
| ISO 9001:2015 | ISO 9001:2008 | Summary of Changes | ||
| 9.3 | Management review | 5.6 | Management review | Title only |
Why undertake management reviews?

- Determine and evaluate QMS performance
- Determine the need for change and improvement
- Determine the suitability of the policies and the objectives
The purpose and final outcome of the management review should be continual improvement of the QMS. As your organization’s QMS increases in its effectiveness and efficiency, your processes performance and improvement process will likewise increase.
When should we schedule a management review?
The frequency or intervals of reviews must be defined in the QMS by the Management Team.

Aim to do a management review at least once a year or more often if appropriate. Little and often is best; there is nothing to say that you have to go through the full agenda each time, nor is there any need to duplicate effort if you cover certain aspects as part of other management meetings.
The frequency of management reviews might be monthly, quarterly, six monthly or annually. You may decide to have stand-alone management reviews or combine it with other business activities, e.g. strategic planning, business planning, operations meetings, process reviews/councils, customer requirements or functional reviews. It is up to your organization to set the format, frequency and intervals of the formal review, but it must be defined in the QMS or related documented procedure.
What should be reviewed?
Customer feedback and Internal and external issues should be discussed, recommendations for improvement - and their potential effect on the strategic direction of the organization.
Free alistair maclean novels. Ulysses up to The Last Frontier) were third-persona narratives, mostly set during WWII and were somewhat epic in tone.
The management review must address the possible need for changes to policy, objectives, targets, and other elements of the QMS.The management review process must ensure that the necessary information is collected ahead of time to allow management to effectively carry out this evaluation.
Internal
- Minutes from previous management reviews
- The policies, objectives and targets
- Results of QMS and process audits
- The extent to which objectives and the numeric targets were met
- Assessment of risk management actions
External
- New or proposed legislation or regulations
- External providers and suppliers performance
- Changing expectations/requirements of relevant interested parties
- New or modified activities, products, or services
- Advances in technology and science
- Changing market preferences of buyers
All management reviews must be documented. Observations, conclusions, and recommendations for further necessary action from the review must be recorded. If any corrective action must be taken, Top management should follow up to ensure that the action was effectively implemented.
The purpose and final outcome of the management review should be continual improvement of the QMS. As your organization’s QMS increases in its effectiveness and efficiency, your environmental performance will likewise increase.
9.3.2 Management Review Inputs (Agenda)
Effective management - The management review process must ensure that the necessary information is collected ahead of time to allow management to effectively perform the review.
The management review process should focus on the following inputs:
- Risks and opportunities (Clause 6.1)
- Possible changes that might affect the system (Clause 6.3)
- External provider and suppliers performance (Clause 8.4)
- Customer satisfaction and perception (Clause 9.1.2)
- Audit results (Clause 9.2)
- Non-conformity and corrective actions (Clause 10.2)
9.3.3 Management Review Outputs (Minutes/Actions)
All management reviews must be documented. Observations, conclusions, and recommendations for further necessary action from the review must be recorded. If any corrective action must be taken, Top management should follow up to ensure that the action was effectively implemented.
Auditors should expect to evidence the same outputs from management reviews as ISO 9001:2008 Clause 5.6.3, however, they should note that the results of management reviews can now be held in any format that the organization chooses.
Typical outputs might include:
- Process improvement actions
- QMS improvement actions
- Product improvement actions
- Resource provision actions
- Revised business plans and budgets
- Changes to quality objectives and policies
- Management meeting minutes
Management review meeting minutes should be retained as documented information.
How's best to document management reviews?
It is not a mandatory requirement to document the management review procedure for achieving ISO 9001:2015 certification, however, if the management review process is vital in achieving product quality; you may find a documented procedure useful.
Develop and implement a management review procedure that defines:
- Management review responsibilities
- Management review scheduling
- Management review inputs
- Management review outputs
Measuring management review effectiveness
The management review process can be measured by assessing the effectiveness of key decisions/outputs; e.g. budgetary changes, forecasts, revised resources plans or changes to the quality policy or objectives.
Download the latest drivers, firmware, and software for your HP LaserJet P1005 Printer.This is HP’s official website that will help automatically detect and download the correct drivers free of cost for your HP Computing and Printing products for Windows and Mac operating system. Hp laserjet p1005 install for windows 10.
Management review outputs are intended to improve your business; auditors will look for evidence that this is being achieved.
ISO 9001 Clauses - CHECK
Iso 9001 2015 Management Review Checklist
An ISO 9001 audit checklist is a tool, one of many in the auditor's toolbox, used to assess an organization's quality management system. Consider an analogy comparing the QMS to a carpenter's blueprint and the auditor to a construction inspector. The goal is to assess the work that's being done in comparison to how the blueprint says it should be done and also in comparison with the building codes -- or, in this case, the ISO 9001 requirements. Checklists should be designed to help with that assessment, not to add red tape.
Documentation Review
A checklist can be designed to perform a documentation review. After confirming that the organization's document control procedure as written meets ISO 9001 requirements, design the checklist by pulling specific items from that procedure. Focus the questions on document control itself, with only one or two questions addressing the ISO 9001 requirements specific to the process being audited. It is enough to ask: 'Which ISO 9001 clause(s) apply to Process ABC?' and 'Does Process ABC meet those requirements?' It is not necessary to rewrite the entire standard as questions on checklists.
Management Responsibility & Commitment
A checklist can be designed specifically for a management audit. The checklist can identify each clause that states a requirement as a direct responsibility of top management and other pertinent items, such as human resource and infrastructure planning. This checklist can be used initially during a management interview and then completed through the course of the audit as evidence is assessed across the organization.
Iso 9001 2015 Management Review Template
Training & Competence
A checklist can prompt auditors to remember universally applicable requirements, such as training and competence. When following an audit trail covering other clauses, these requirements can sometimes be overlooked and require follow-up activity before the audit can be closed. A checklist can help ensure that auditors look for evidence that employees are competent for the jobs they perform based on education, training, skills and experience. Equally important is to confirm that action plans are developed and carried out to ensure that employees achieve the levels of competence needed.
Outsourced Processes
Checklist items should cover outsourced processes. This may be combined with the universally applicable requirements noted above. The adage 'out of sight, out of mind' can cause both auditees and auditors to forget that warehousing for Programs A, B and C is still done on site, but for Program X that function is now performed by a third-party logistics provider. ISO 9001 specifically requires that outsourced processes be controlled to ensure that they meet the organization's own QMS requirements.
Monitoring & Measurement
Iso 9001 Management Review Checklist Form
Checklists should address measuring process effectiveness and monitoring trends to assess the capability of the QMS. Measures can include complex statistical process control data or can be as simple as the number of internal or external customer complaints. Checklists should enable auditors to identify what metrics are in place and what trends those metrics have revealed since the previous audit. Checklists should also remind auditors to look for evidence of action taken to correct negative trends.
Iso 9001 2015 Checklist Pdf
Add Value
Audit checklists should add value rather than exist for the mere sake of meeting an internal audit process requirement. It is more important for an auditor to follow an audit trail that presents itself during the audit than to follow a checklist. Inexperienced auditors can lose sight of such trails when they rely too heavily on checklists.
Cisco's Binary Number game has been brought back with our adaptation. Learn how to convert binary to decimal and vice versa with this fast-paced 'Easy to learn, hard to master' game about binary numbers. Dec 31, 2016 ( In case you didn't ever use it, that Cisco game was a lot of fun, until Cisco removed it from its open website recently!) Related Videos Cisco Networking Academy. Nov 30, 2016 Many computer science teachers have used Cisco’s popular game to help reinforce their binary numbers lessons. Cisco has removed the game! We here at Penjee have created our own version of the Cisco Binary Number Game here! It’s free., requires no loginning in and we think our adaptation is as fun as Cisco’s original version. Embed this game. Learn Python with Penjee Binary Calculator Why do computers use binary? Cisco Binary Number Game. Sort Detective. Many computer science teachers have used Cisco’s popular game to help reinforce their binary numbers lessons. Cisco has removed the game! We here at Penjee have created our own version of the Cisco Binary Number Game here! It’s free., requires no loginning in. Binary blitz game.
Quality Management Review Template
- Mel Stoutsenberger/iStock/Getty Images




